Even the worst mass extinction had its oases
Plants thrived in present-day China throughout the End-Permian extinction.
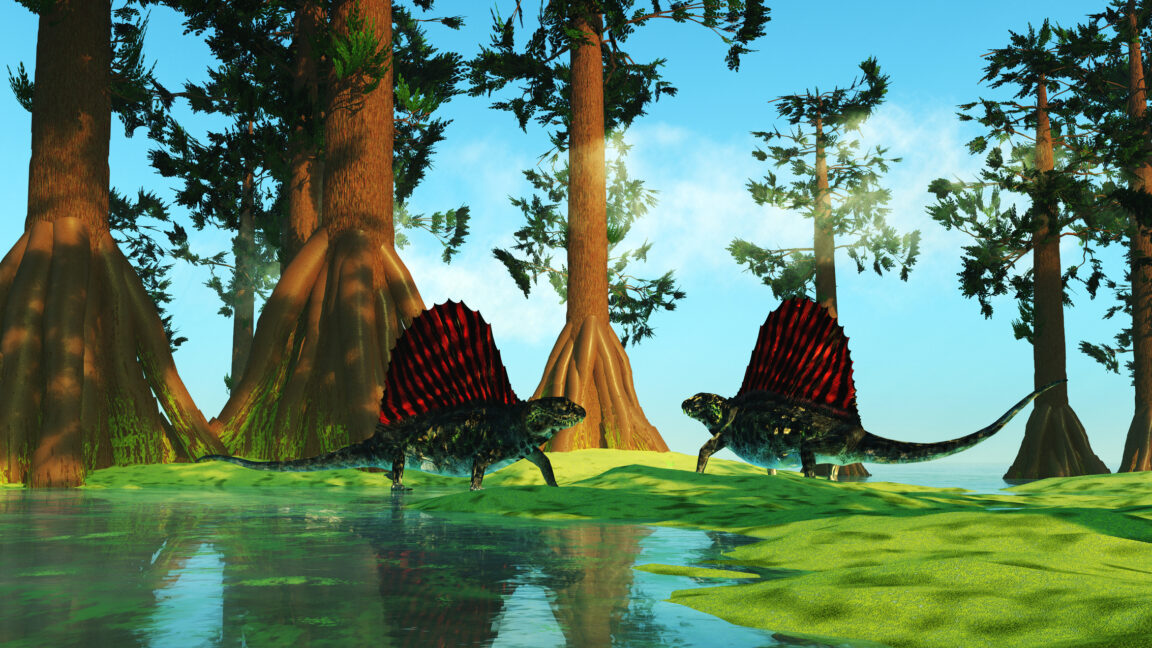

About 252 million years ago, volcanic eruptions triggered the End-Permian Mass Extinction, also known as the Great Dying. About 96 percent of marine species were wiped out—but were things just as grim on land?
Scientists have debated whether this event caused nearly as much terrestrial destruction. Now, researchers from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology (NIGPAS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences suggest that terrestrial ecosystems did not suffer nearly as much as the oceans.
Led by paleontologist Feng Liu, the NIGPAS team found evidence for refugiums, oases where life thrived despite the devastation. Not only did these refugiums give life a chance to survive the mass extinction event, which lasted 200,000 years, but they are now thought to have been crucial to rebuilding ecosystems in much less time than was previously assumed.